Before jumping into AWS Elastic Load balancer, first we
need to understand, what is the Need of
Load balancer in IT World.
1. Load balancer
Lets start with a problem statement
to understand the Load balancer.
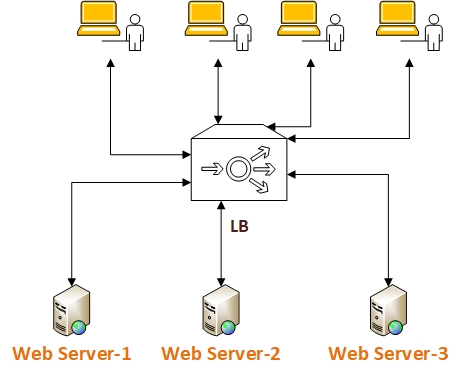
Problem Statement
I have
website, which is hosts only one webserver, when heavy incoming application traffic
comes, the webserver cannot handle this traffic.
Solution
To
overcome this problem, we need some mechanism, in which we have a website hosted
on more than one servers and distribute the high heavy incoming application traffic
between servers to reduce the load on single server.
To
implement this mechanism Load balancer comes into the picture.
Load
Balancer can be “Internet facing” or
Internal one. If Load balancer has public
resolvable DNS name, then it is called “Internet
Facing” Load Balancer otherwise it is called “Internal” Load Balancer.
Below are
some benefits to implement the Load balancer.
a. Optimize
resource use.
b. Maximize throughput.
c. Minimize
response time
d. Avoid
overload of any single webserver
e. Help to
create Fault tolerance and High availability application
2. AWS
Elastic Load Balancer
AWS
Elastic Load balancer is AWS managed Load balancer service, which distributes
the web traffic to available web servers. AWS provided three types of Load balancers.
e.g. Classic Load Balancer, Application Load Balancer and Network Load Balancer.
It is
regional Service and comes under EC2 service section in AWS Console.
2.A. Classic Load Balancer (CLB)
1. AWS refers
this Load balancer type as the “Previous generation” and I think it will be
phased out soon.
2. It
supports HTTP, HTTPS, TCP, SSL/TLS Protocol for communication.
3. CLB works
on L4(Transport) and L7 (Application) layer of the OSI model.
4. It supports
all ports 1 to 65535.
5. Its
supports IPV4 address in a VPC.
6. It
does not support HTTP/2 and WebSocket.
7.
CLB name is
unique in AWS account in a region.
8.
You can
create maximum 20 Classic Load balancer per region.
9.
Classic
Load Balancer Listeners (CLB Listeners)
a. Listeners
is the process which checks the connection request base on protocol (HTTP, HTTPS, TCP, SSL/TLS) and port.
You need to provide the listeners configuration while creating the Elastic Load
Balancer.
Actually, when you create the CLB, it automatically creates the Nodes.
Nodes have ENI and IP address. Nodes Pick IP address from Subnet which is assigned
to CLB. These Nodes are also known as CLB nodes.
b. CLB have
two types of Listeners.
Front-End Listeners
1. It
receives traffic from the Client and send it to Back-End Listeners, based on
protocol and port.
2. It
receives response from Back-End Listeners and send it to the Client.
Back-End Listeners
1. It
receives traffic from Front-End Listeners and send it to Webserver, based on
protocol and port.
2. It receives response from Webserver and send
it to Front-End Listeners.
c. Below is
the configuration property of CLB Listeners in AWS.
1. Load Balancer Protocol
This is the protocol information for
Front-End Listeners.
2. Load Balancer Port
This is the port information for Front-End
Listeners.
3. Instance Protocol
This is the protocol information for
Back-End Listeners.
4. Instance ports
This is the port information for Back-End
Listeners.
10. To
distribute the traffic from CLB to EC2 instances, we need to register these EC2
Instances with CLB. These Instances are called Register Instances. As Classic Load balancer(CLB) is Regional Service,
So ELB and EC2 Instances should be in the same VPC.
11. You can
register maximum 1000 Instances from a load balancer.
12. CLB
transfers the traffic only to primary/Default ENI (Eth0) to registered EC2
Instances.
13. If Eth0 have multiple IP, then Load
Balancer can transfer the traffic to primary IP only.
14. To Create
the CLB, we have to provide the Subnets. This Subnets is used to create the Load Balancer Nodes and assign one IP
address from assigned Subnet.
a. You can
assign multiple subnet to Load balancer, but you can assign only one subnet in
an Availability Zone at a given time. If you try to assign multiple Subnets to
Load Balancer from an Availability Zone, it overwrites the previous one.
b. AWS
recommends that Subnet Size should be greater than or equal /27 size and at least 8 available IP
for Load Balancer Nodes.
c. If you
register EC2 Instances from any Availability Zone, but forget to add Subnet
from that Availability Zone for Load balancer node, then These Availability
Zone Instances will not receive the traffic.
15. For Fault
tolerance, you should distribute your EC2 Instance in multiple availability
Zones.
16. Heath Check
a. CLB also
checks the status of registered EC2 Instance and marks them “Healthy” and “Un-Healthy”.
b. Healthy
Instance shows as In-Service under CLB.
c. Un-Healthy
Instance shows as Out-of-Service
under CLB.
e.
When you
create CLB from AWS Console, By Default it uses ping, HTTP on port 80 for
health-check of registered EC2 Instances. You can change it.
f.
When you
create CLB from AWS API, it uses ping, TCP on port 80 for health-check of
registered EC2 Instances. You can change it.
g.
Default Response
timeout (Idle Timeout) is 5 Second, means Load balancer waits for 5 seconds for
a health check response, if not received response in this time frame then it treats
this Health-check as failed. you can change this value from 2 to 60 seconds.
h. Un-Healthy Threshold
Number of consecutive Failed “health-check” is Un-Healthy Threshold. The Default value of Un-Healthy Threshold is 2 But you can change this value from 2 to 10.
i. Health Check Interval
This is the time period between two consecutive health check. Default value is 30 seconds and you can
change this value from 5 to 300 seconds.
j. Healthy Threshold
Once Instance is marked as
Out-Of-Service then number of consecutive successful health check is Healthy Threshold. The Default value
of Healthy Threshold is 10 But you can
change this value from 2 to 10.
17. For Internet
facing CLB, assigned subnet to Load Balancer should be in Public Subnet
otherwise LB will not work.
Below is the DNS format for Internet facing Load balancer.
Format: LBName-1234567890.RegionName.elb.amazonaws.com
Example: myinternetfacingelb.1234567890.eu-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com
18. For
Internal CLB, assigned subnet to Load Balancer should be in private Subnet.
Below is the DNS format for Internal Load balancer.
Format: Internal-LBName-123456789.RegionName.elb.amazonaws.com
Example:internal-myinternalfacingelb.123456789.eu-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com
19. You can
add TAGs in Load Balancer.
20. Auto Scaling Group with CLB
You can associate the Classic load balancer with the Auto Scaling
group. Classic Load balancer and Auto Scaling works in harmony.
21. Cross Zone Load balancing
a. When we
register EC2 Instances from different availability Zones, Load Balancer
distributes the traffic evenly between these availability Zones. It does not
consider, how many EC2 Instances are registered in each availability Zones.
Example: Like if
we have registered 6 Instances. Out of six, four are from availability Zone1
and two are from availability Zone-2. CLB distributes the traffic 50% to Fours
Instances in Availability Zone-1 and 50% to two Instances in Availability Zone -2.
b. If you
want to distribute the traffic evenly between all registered EC2 instances,
then you should enable the “Cross-Zone Load Balancing” property.
c. While creating
CLB from AWS Console, the option to enable cross-zone load balancing is
selected by default and can change it.
d. If you are
creating CLB from API/SDK, Cross Zone Load Balancing property is Disabled by
default and can change it.
e. AWS does not
charge for regional data transfer between Availability Zones when you enable
cross-zone load balancing in CLB.
22. Connection Draining
a. When CLB
identifies an un-healthy instance, it waits for a specific time period to
complete the in-flight session before marking this un-healthy. This period is
called the Connection Draining time period. CLB does not send any new traffic
for this Instance.
b. During
Connection Draining time period, EC2 instance’s state will be “In-Service”
only.
c. After a “Connection
Draining” time period, CLB terminates the session and markes Instance as un-healthy.
k. While
creating CLB from AWS Console, the option to enable Connection draining is selected
by default with 300 second’s period. You can uncheck it and also change the
time period.
l. If you are creating CLB from API/SDK,
Connection draining property is Disabled by default and but you can change it
later.
23. Security Group
a.
You can
assign the Security Group on CLB. With help of this, you can control the
Traffic from Client to Front-end Listener. Also helps to control traffic from
Back-end listener to EC2 Instances.
b.
You can
assign maximum 5 Security groups.
c.
At least one
security group is required to create the CLB.
24. Classic Load Balancer Access Log
a. If you
want to capture the request information which is sent to your Classic Load
Balancer, then “Access Log” is your answer.
b. Access log
is disabled by default. Access Log contains below information which can be used
further for analyze purpose.
1. Request
Time
2. Client IP
Address
3. Latencies
4. Request
Path
5. Response
c. You can
store the access log on S3.
d. AWS does
not extra charge for enabling the access log.
25. HTTPS Traffic
a. To use
HTTPS communication over the CLB, you have to enable X.509 SSL/TLS Certificate on the load balancer. TLS is the updated
version of SSL.
b. CLB
supports TLS/SSL.
c. CLB
received HTTPS traffic from the Client and terminate the HTTPS connection at
Load balancer end (Listener end) and decrypt the message. This is called SSL
termination or SSL offloading.
After SSL
Termination, you can send the unencrypted traffic to EC2 Instance via HTTP
protocol. If you want to send encrypted message to EC2 Instance as well then, in
this case CLB again encrypt the message and send it to EC2 Instance via HTTPS
protocol.
26. Cloud Watch
a. CLB
publishes the data to CloudWatch for
itself and register instances with it.
b. CLB sends
Load Balancer metrics data at every one minute of interval.
c. Cloud
Watch can use these metrics data to send Notification via SNS service.
27. You can
enable CloudTrail Log for your
Classic Load Balancer.
28. When
Traffic Increases, Classic Load Balancer increase the ELB nodes automatically
according to the associated Subnet but it can take 1 minutes to 7 minutes to
scale.
29. CLB cannot
queue the requests, If It receives request more than its capacity request, then
request gets failed and Load balancer return HTTP 505 Error.
30. Sticky Session
a. By
Default, CLB send each request to register in-service EC2 instance which has
least load.
b. If you
want to bind the user session with specific EC2 instance, then CLB Sticky
Session feature is your answer.
c. Sticky
Session works with HTTP and HTTPS work load only.
d. You cannot
find this property while creating the CLB, you have to Edit the Load balancer
to enable this features.
e. Sticky
session feature use cookies. CLB use two type of cookies.
1. Application
Cookies.
2. Load
Balancer duration based cookies.
31. CLB does
not support “Delete Protection” feature, which can lead deletion of Load Balancer accidently.
32. CLB
Supports SSL Offloading.
2.B. Application Load Balancer (ALB)
AWS
created separate Load Balancer for L7 Layer (HTTP and HTTPS) with additional
features in 2016. Amazon refers this as Application Load balancer.
Some
properties are same as Classic Load Balancer(CLB) but we will discuss all the
properties and features again with respect to Application Load balancer(ALB) to
avoid the confusion.
1. ALB
supports content based Routing (Path/Domain based), Means you can forward the
request to Webserver, based on request URL and request HTTP header properties.
We will discuss this in detail later in this Blog.
2. ALB
supports containerized applications.
3. It
supports HTTP, HTTPS, HTTP/2 and WebSocket.
4. WebSocket
supports full duplex Communication and it is enabled by Default. It can be used
with HTTP and HTTPS Listeners.
5. HTTP/2 is
used to send multiple request at the same time.
6. Like CLB,
Application Load balancer(ALB) support TLS/SSL.
7. Target
It is a Webserver, where you have hosted your web application on
HTTP/HTTPS. You can use below endpoints as Targets.
a. EC2 Instances
1.
Same VPC
EC2 Instances.
2.
Traffic
is forwarded to EC2 Instances through primary NIC (Eth0) and primary IP only.
b. IP Address
1. You can
use any IP from VPC.
2. You can
use IP from Peering VPC.
3. You can
use IP from on-Prem server, which is integrated with AWS from direct connect or
AWS VPN.
4. Any AWS
resource which can be accessed by IP address and port.
5. You can
specify any private IP address of any NIC attached to the Server.
c. Lambda
Function.
d. Application
on ECS Instance.
8. Target Group
a. It is
Logical grouping of Targets.
b. It is
regional entity, so you can group only those targets, which exist in same
region as Target group.
c. You can
add one Target group with one Load balancer at a given time.
d. You can
add up to 200 targets in a target group.
e. Target
group is independent from load balancer, means if you delete the Load Balancer,
Target group is not deleted automatically.
f.
One Target can map with multiple Target Groups.
g. You need
to specify Port and protocol for each target group.
h. One Target
also maps multiple time with the same Target group, but port and protocol
should be different, while registering it again with the same Target group.
i.
Target group and ALB are independent, if you
delete the ALB then target group is not deleted automatically, you have to
delete it separately.
j.
Health
Check
1. Health
check is done at the Target Group level.
2. Healthy
Instance show as Healthy under Target Group.
3. Un-Healthy
Instance show as Un-Healthy under Target Group.
4. Target
Group does not route the traffic to un-healthy Target.
5. By Default,
it uses “ping HTTP” on port 80 for health check of Target in Target group. You
can change it.
6. Default
response timeout (Idle Timeout) is 5 Seconds, means Target Group waits 5
seconds for a health check response, if not received response in this time
frame then treats this Health check as failed. you can change this value from 2
to 60 seconds.
7. Un-Healthy Threshold
Number of consecutive
Failed “health check” is Un-Healthy Threshold. The default value of Un-Healthy Threshold is 2 seconds, but you
can change this value from 2 to 10 seconds.
8. Health Check Interval
This is the time period
between two consecutive health check. The default value is 30 seconds and you
can change this value from 5 to 300 seconds.
9. Healthy Threshold
Once Instance marked as Out-Of-Service then number of consecutive
successful health check is Healthy Threshold.
The default value of
Healthy Threshold is 5 seconds, but you can change this value from 2 to
10 seconds.
k. Below is
the limit of Targets in Target group.
1. You can
add maximum 1000 IP address or Instances.
2. You can
add 1 Lambda function.
l.
You can also attach Auto Scaling group with
Target Groups to create EC2 Instances automatically as per Load.
9. ALB Listeners
a. Unlike CLB,
we don’t have listener types, like Front-End and Back-End. There is only one listener
which checks the request and forward it to one or more target group based on
rules. Target Groups forwards the request to registered target based round
robin routing algorithm.
b. ALB
listener supports below protocol.
1. HTTP
2. HTTPS
c. Supports
all ports from 1 to 65535.
d. You can
create up to 50 Listeners per ALB.
10. ALB Listeners Rule
a. You need
to define the Listener rule to select the appropriate Target group, By Default,
“Default Rule” is created which send the request to Default Target Group, while
creating the ALB. So at the time of creation of ALB, AWS allows to create the
Default Rule only.
b. If you
want to create more rules then, you need to Edit the ALB and add/update the Listener
rules.
c. Every Rule
has a priority and You can change the priority of any rule any time, except the
Default Rule
d. Default
rule executes at Last.
f. ALB supports
redirecting/Forward requests from one URL to another via Listeners Rules.
11. Security Group
a. Like CLB,
you can apply security group on the ALB.
b. You can
assign maximum 5 Security groups.
c. At least
one security group is required.
12. You can
add TAGs in Load Balancer.
13. Cross Zone Load balancing
Cross Zone Load balancing is by default enabled and you cannot
disable it.
14. Connection Draining
a. Overall
concept of Connection Draining concept is similar to CLB.
b. Unlike CLB,
you cannot find “Connection Draining”
option while creating ALB. So This property is
disabled by default. To enable this property first, you have to create the ALB,
then Edit Load balancer and you will find “Connection Draining” property under
description TAB.
15. Sticky Session
a. Concept is
same like CLB to distribute the traffic of same user traffic to same Target.
1. It supports
Load balancer cookies only. Application level cookies are not supported by ALB.
It is enabled by default.
2. Name of
property is “Load Balancer duration” based on cookies
3. Load
balancer Creates Cookies with Name is AWSALB.
16. Cloud Watch
It is same as CLB, but Health Check is done at Target Group Level
and its more enhanced then Classic Load Balancer.
17. Routing
a. Apart from
Port and Protocol of request, you can also use other request parameter to decide
the Target groups. AWS calls this Content based routing.
b. Application
Load balancer supports two types of Content Based Routing.
1. Host Based /Domain Based Routing
Based on Domain URL like “xyz.com” of request and port(optional),
you can decide the Target group to serve this request.
Example:
a. If Domain
URL is “xyz.com1” then it will go Target Group-1 and if Domain URL is “xyz.com2”
then it will go Target Group-2.
b. If Domain
URL is “xyz.com” with Port -80 then it will go Target Group-1 and if Domain URL
is “xyz.com” with port -443 then it will go Target Group-2.
2. Path Based Routing
The Load balancer can select the Target group with help of path
element of URL the request.
Example: Means if
Request URL have “Images” in path it will go “Target Group-1”.
c. You can
use a combination of Host based routing and Path Based routing to decide the Target
Groups.
d. If Any
rule is not matched, then the request will sent to Default Target group.
e. You can
use Below request field in Routing.
1. Standard
HTTP Header
2. Custom
HTTP header
3. Method
Name
4. Query
parameters
5. Source IP
Address
6. Host Name
(Used in Host based Routing)
18. Application
Load Balancer supports “Delete Protection” feature, which prevents deletion
of Load Balancer accidently. It is disabled by default.
19. Application Load Balancer Access Log
1. This
feature is same as CLB, but provide more information in Access log in comparison
to CLB and the access log stored in compressed format.
2. When ALB
receives the request, it Adds/updates the x-Amzn-Trace-ID
header and can be logged in the access log. With the help of this you can track
the request from Client to Target and other services.
20. ALB can
integrate with WAF (Web Application Firewall) to allow and Block request based
on rules (Web ACL).
21. Internet
Facing Application Load balancer supports both IPV4 and IPV6 address in
selected Subnet.
22. Internal
Application load balancer supports IPV4 address only.
23. ALB
Supports SSL Offloading.
24. ALB
supports Server Name Indication (SNI). SNI is the component of SSL, which allows
us to host multiple website on one IP
address and each website have its own SSL/TLS certificate. Without SNI, Each
Hostname is required, separate IP address in order for an SSL certificate to be
installed.
25. ALB can
integrate with Amazon Cognito service
for user authentication.
2.C. Network Load Balancer(NLB)
AWS created separate Load Balancer for L4
Layer (TCP, UDP and TLS) with additional features in 2017. Amazon refers this
as Network Load balancer.
1. NLB
Supports TCP, TLS and UDP protocol.
2. NLB
Supports SSL/TLS Certificate.
3. NLB
provides low latency as compared to other AWS Load Balancer. It has higher
connection rate compared to other Load Balancer and Can handle millions of requests
per seconds.
4. Target
You can use below endpoints as Targets.
a. EC2 Instances
1. Same VPC
EC2 Instances.
2. Traffic
forwards to EC2 Instances through primary NIC (Eth0) and primary IP only.
b. IP Address
1. You can
use any IP from VPC.
2. You can
use IP from Peering VPC
3. You can
use IP from on-Prem server, which is integrated with AWS from direct connect or
AWS VPN but Should Follow CIDR range RFC1918 and RFC6596.
4. You can
specify any private IP address of any NIC attached to the Server.
5. Target Group
a. Same
Concept which we have discussed in ALB. It is Logical grouping of Targets.
b. You can attach
Auto Scaling group with Target Groups to create EC2 Instances automatically as
per Load.
6. Health Check
a. Health
check is done at the Target Group level.
b. By
Default, it uses “ping TCP” on port 80 for health check of Target in Target
group. You can change it.
c. Default
response timeout (Idle Timeout) is 10 Second.
d. Default
value of Un-Healthy Threshold is 3
seconds.
e. Health Check Interval
It can be either 30 Seconds
or 10 Seconds, Default is 30 seconds.
f.
Healthy
Threshold
Default value of Healthy
Threshold is 3 But you can change this value from 2 to 10.
7. NLB Listeners
a. Concept is
same as ALB. There is only one listener which checks the request and forwards
to one or more target group based on rules.
b. NLB
listeners support below protocol.
1. TCP
2. TLS
3. UDP
4. TCP_UDP: It is used when, if you want TCP and UDP
protocol communication on the same port, but Target group for a TCP_UDP
listener must use TCP_UDP protocol.
c. Supports
all ports from 1 to 65535.
d. You can
create up to 50 Listeners per load balancer.
e. NLB
Listener supports Elastic IP as well.
f.
You can use WebSocket with Listeners.
g. If
Listener supports TLS, then you must deploy exactly one SSL/TLS server certificate
per Listener.
8. NLB Listeners Rule
Same concept as Application Load Balancer.
9. Security Group
a. You cannot
apply Security group on NLB, means you cannot filter the data at Load balancer
level, it should be filtered by EC2 or Subnet level.
10. You can
add TAGs in Load Balancer.
11. Cross Zone Load balancing
Cross Zone Load balancing
is Disabled by default and you can enable it.
12. Connection Draining
a. It is same
as ALB. You can find this under Target group name as “Deregistration Delay”.
13. Sticky Session
b. Sticky
Session property is not applicable for NLB.
14. Cloud Watch
a. Same
concept as ALB.
15. Routing
Network Load Balancer does not support Routing (Path, Content
etc.) like ALB.
16. Network
Load Balancer supports “Delete Protection” feature, which prevents deletion of Load
Balancer accidently. It is Disabled by default.
17. Network
Load Balancer Access Log.
18. NLB
support AWS PrivateLink for
communication.
19. NLB
Supports SSL Offloading.
. 2.D. Features Comparison (CLB VS ALB VS NLB)
Features
|
CLB
|
ALB
|
NLB
|
Protocol
|
HTTP, HTTPS ,TCP ,SSL/TLS
|
HTTP , HTTPS
|
TCP , UDP
|
Layer Support
|
L4 and L7
|
L7
|
L4
|
IPV4 Support
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
IPV6 Support
|
No
|
Yes
|
No
|
HTTP/2
|
No
|
YES
|
No
|
WebSocket
|
No
|
YES
|
YES
|
Health-Check
|
EC2 Level
|
Target Group Level
|
Target Group Level
|
Auto Scaling Group
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Cross Zone Load Balancing
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Connection Draining
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Security Group Support
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
No
|
Access Log
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
CloudWatch Integration
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Sticky Session
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
No
|
Delete Protection
|
No
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
VPC PrivateLink support
|
No
|
No
|
Yes
|
Content Based Routing
|
No
|
Yes
|
No
|
URL Re-direction
|
No
|
Yes
|
No
|
Lambda Function as Target
|
No
|
Yes
|
No
|
SSL Off-loading
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
SNI Support
|
No
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
WAF Integration
|
No
|
Yes
|
No
|
Back-end Server Encryption
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
User Authentication
|
No
|
Yes
|
No
|
Back-end server authentication
|
Yes
|
No
|
No
|













Valuable post useful for everyone.Keep on sharing.
ReplyDeleteAWS Training
AWS Online Training
Amazon Web Services Online Training
Hey thanks for this amazing post! Thank you so much for sharing the good post, I appreciate your hard work.Keep blogging.
ReplyDeleteDevOps Training
DevOps Online Training
Thanks for sharing this Information. AWS Training Institute in Gurgaon
ReplyDeleteThis is a very nice one and gives in-depth information. I am really happy with the quality and presentation of the article. I’d really like to appreciate the efforts you get with writing this post. Thanks for sharing.
ReplyDeleteAWS classes in Pune
We can share this blog to anyone related to this topic. Thanks for sharing.
ReplyDeleteAWS Certification in Chennai
Learn AWS Online
Best AWS Training in Bangalore
Thanks for Sharing the AWS or Amazon Web Services Career's Training Courses and Certificates for Freshers and Experience Candidates.
ReplyDeleteAWS Training in Bangalore
Best AWS Training Institutes in Bangalore
Cloud Computing courses in Bangalore
AWS course in Bangalore
Thanks you and excellent and good to see the best software training courses for freshers and experience candidates to upgade the next level in an Software Industries Technologies,
ReplyDeleteAWS Training in Bangalore
AWS course in Bangalore
Best AWS Training Institutes in Bangalore
Cloud Computing courses in Bangalore
Thanks you and excellent and good to see the best software training courses for freshers and experience candidates to upgade the next level in an Software Industries Technologies,
ReplyDeleteAWS Training in Bangalore
AWS course in Bangalore
AWS Training Bangalore
AWS course Bangalore
Thanks You for Share,
ReplyDeleteAWS Training in Bangalore
AWS course in Bangalore
AWS Online Training in Bangalore
AWS Online Courses in Bangalore
AWS Training Institutes in Bangalore
Cloud Computing courses in Bangalore
Genex's specialized DBA consultants help you navigate data strategy. The support of database consultants ensures optimal administration, yielding, availability, funds, supervision, and security. With us, your database will be designed, transferred, maintained, backed up, recovered, and architected. Our well-experienced professionals will help you to manage powerful relational database management.
ReplyDeletehttps://genexdbs.com/
Thank you for sharing wonderful information with us to get some idea about that content.
ReplyDeleteBest AWS Training Online
Aws Devops Training Online
slot siteleri
ReplyDeletekralbet
betpark
tipobet
betmatik
kibris bahis siteleri
poker siteleri
bonus veren siteler
mobil ödeme bahis
BQXY
tekirdağ evden eve nakliyat
ReplyDeletekocaeli evden eve nakliyat
yozgat evden eve nakliyat
osmaniye evden eve nakliyat
amasya evden eve nakliyat
1CK03B
شركة عزل اسطح بالقويعية
ReplyDeleteZ3mpPghm2m
شركة تنظيف مكيفات بالخبر
ReplyDeletenYzva4
شركة تنظيف بالاحساء
ReplyDeleteBWu9LCtzi5ZQQ